40 orbital diagram of carbon
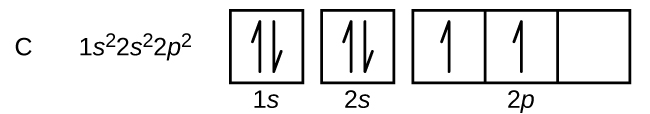
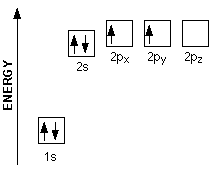
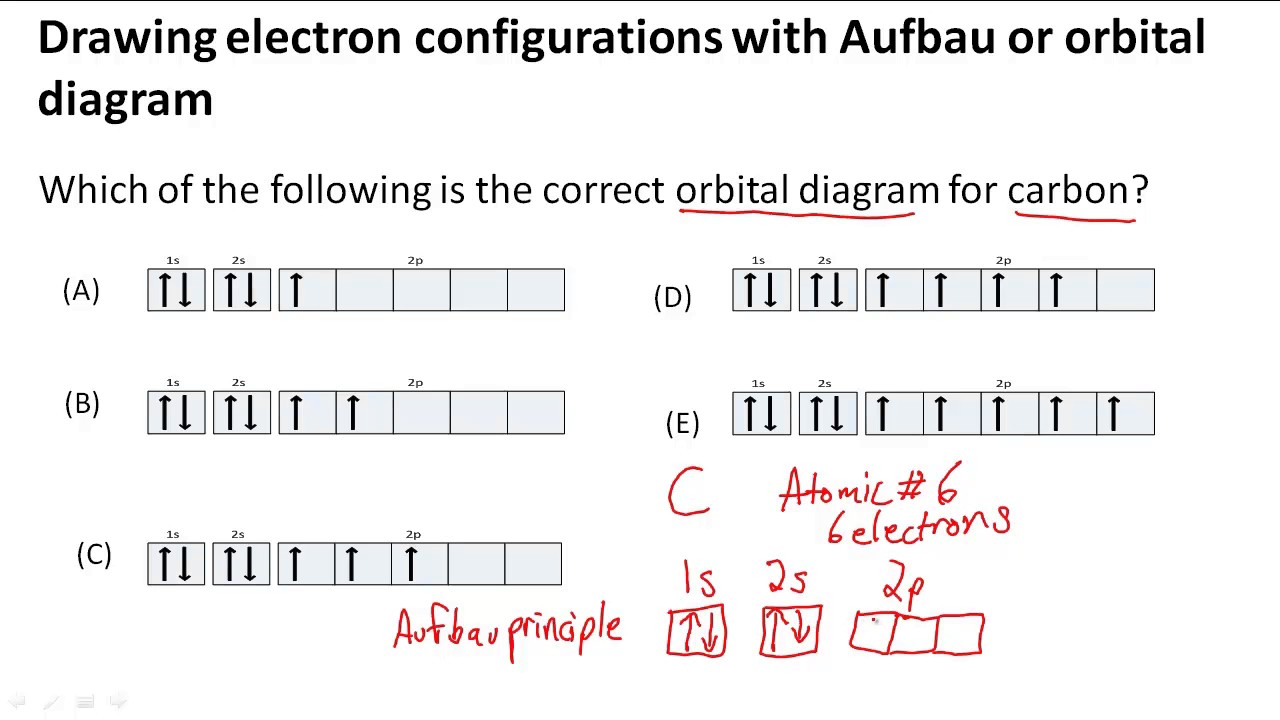
How do you write the orbital diagram for carbon? | Socratic The atomic number of carbon is #6#, which is also the number of positively charged protons its atomic nuclei. If the atom is neutral, it will have the same number of negatively charged electrons. Its electron configuration is #"1s"^2"2s"^2"2p"^2"#. The orbital diagram shows how the electrons are arranged... What is the orbital diagram for carbon? - Answers The orbital diagram can be derived from the elemental carbon's (C) electron (e-) configuration. C is configured as a helium (He) core as [He]2s^2 2p^2, 2, 4. A Lewis dot structure would have a C with one dot, representing a valence electron over each of four sides. A C bonded to 4-hydrogens (H) is CH4...
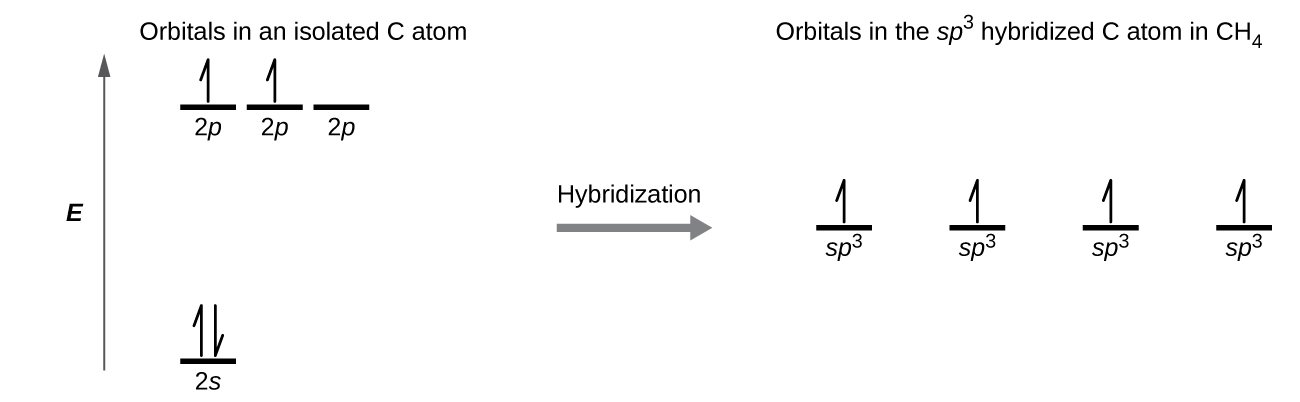
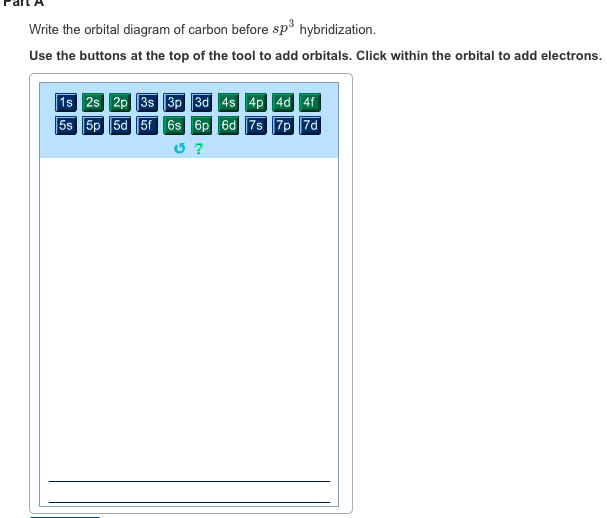
Write The Orbital Diagram Of Carbon Before Sp3 Hybridization Each of the carbons in ethane has four single bonds so each carbon in ethane is sp three hybridized so let me go ahead and put sp three hyb...

Orbital diagram of carbon
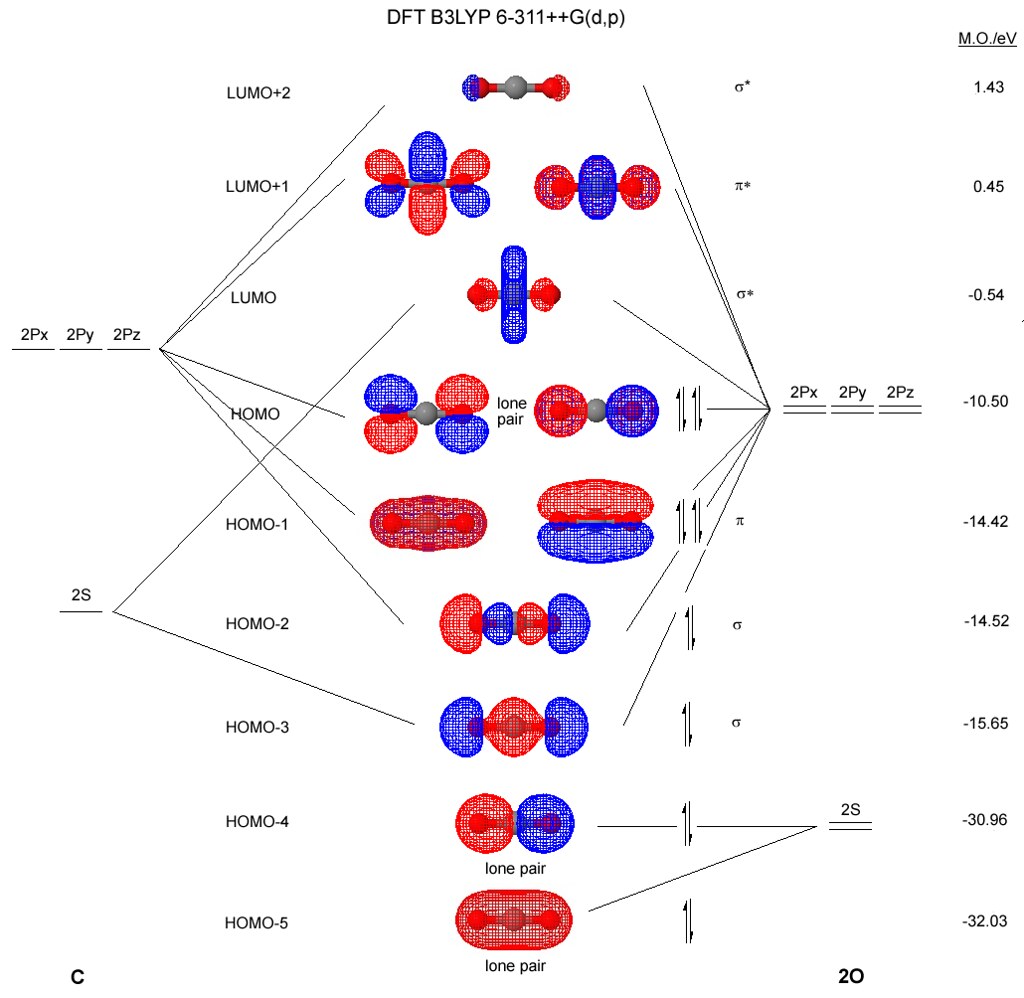
PDF Organometallic Chemistry Prepare a molecular orbital energy level diagram of the peroxide ion, O22−, and predict the bond order of this ion. Group orbital 1 can interact with the 2pz orbital of carbon. (This interaction is likely to be weak, because the 2s orbitals of oxygen are much lower in energy than the 2p orbitals of carbon.) Give orbital diagram of carbon . FOR ONE MARKS - Brainly.in The orbital diagram shows how the electrons are arranged within each sublevel. ... In a neutral carbon atom, the 1s sublevel has one orbital with two electrons with opposite spins, represented by the arrows pointing in opposite directions. Molecular Orbital Theory | Boundless Chemistry Molecular orbital diagram for hydrogen: For a diatomic molecule, an MO diagram effectively shows the energetics of the bond between the two atoms, whose AO unbonded energies are shown on the sides. The unbonded energy levels are higher than those of the bound molecule, which is the energetically-favored configuration. Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals. A …
Orbital diagram of carbon. Carbon(C) electron configuration and orbital diagram Carbon is the 6th element in the periodic table and its symbol is 'C'. This article gives an idea about the electron configuration of carbon and the orbital diagram, period and groups, valency and valence electrons of carbon, bond formation, compound formation, application of different principles. Carbon Orbital Diagram - Free Catalogs A to Z Carbon Monoxide Molecular Orbital Diagram Explanation. Just Now Carbon Monoxide Molecular Orbital Diagram Explanation. generic s-p valence MO diagram for carbon monoxide CO chain one can reasonably explain, that the HOMO of carbon monoxide must be of. SOLVED:Draw the orbital diagram for carbon in \mathrm{CO}... And what orbital here is a new hybridized. This is um, hi brie diced mm pick. So so this is a orbital diagram of carbon in so to an indication of carbon atoms explanation for the given California, all of you to in tiger Ron of carbon in co. two and indication of carbon atoms electrons in each orbital and... Electron configuration for Cobalt (element 27). Orbital diagram Electronic configuration of the Cobalt atom in ascending order of orbital energies: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d7. Below is the electronic diagram of the Cobalt atom.
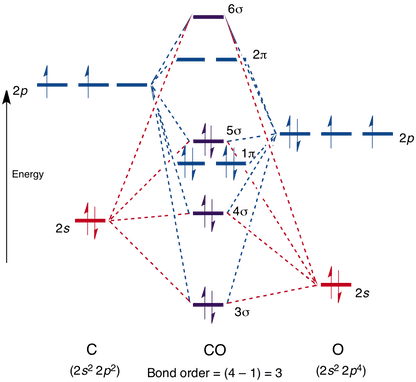
Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry/Molecular Orbital Theory... Valence bond (VB) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons. Molecular orbital diagram of carbon monoxide Carbon monoxide facts, formula, uses, bonding and properties Hybridization, molecular orbital diagram, production and chemical reaction carbon monoxide. Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a colurless, odourless, poisonous gas produced by burning carbon in insufficient oxygen. Orbital hybridisation - Wikipedia Other carbon compounds and other molecules may be explained in a similar way. For example, ethene (C 2 H 4) has a double bond between the carbons. For this molecule, carbon sp 2 hybridises, because one π (pi) bond is required for the double bond between the carbons and only three σ bonds are formed per carbon atom. In sp 2 hybridisation the 2s orbital is mixed … Carbon orbital diagram - Big Chemical Encyclopedia Carbon orbital diagram. With the next element, carbon, a complication arises. In which orbital should the sixth electron go It could go in the same orbital as the other 2p electron, in which case it would have to have the opposite Considering the molecular orbital diagram of carbon monoxide (Fig.
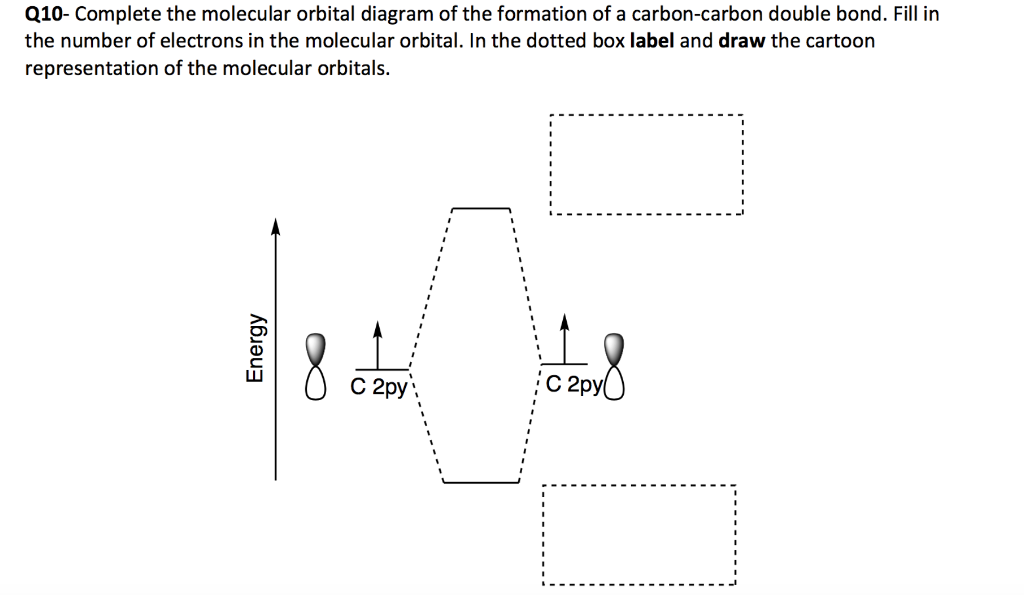
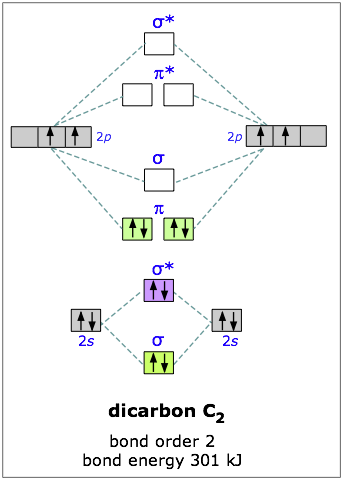
Molecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine … 8.4 Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry Molecular Orbital Diagrams, Bond Order, and Number of Unpaired Electrons Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule, O2. From the molecular orbital diagram of N2, predict its bond order and whether it is diamagnetic or paramagnetic. Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2: Home Watching the Earth breathe from space... Measuring carbon dioxide from space What is the molecular orbital energy diagram of CO? - Quora Here is the molecular orbital diagram of CN-: There are 8 bonding electrons and 2 antibonding electrons, therefore. Orbital overlaps now occur between the 1s orbital on both H atoms and 2 of the carbons sp2 HAO's, to form two pairs of bonding and anti bonding molecular orbitals.
File:Orbital diagram carbon - Hund's Rule.svg - Wikimedia Commons English: Orbital diagram for carbon, showing the correct application of Hund's Rule. Date. The following other wikis use this file: Usage on en.wikibooks.org. High School Chemistry/Orbital Configurations.
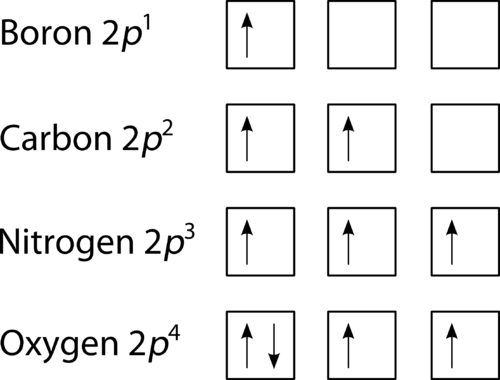
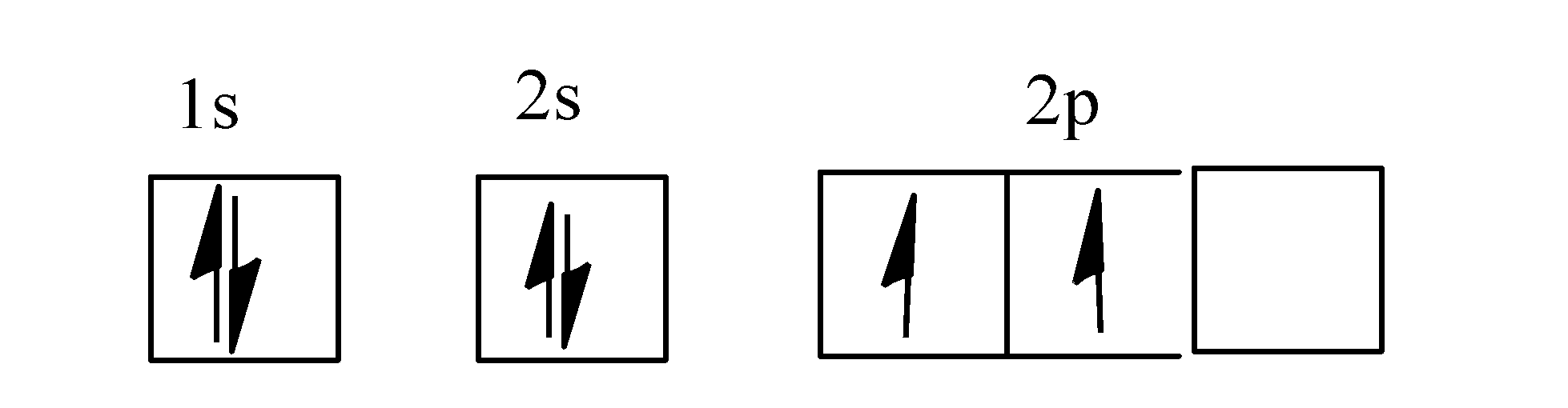
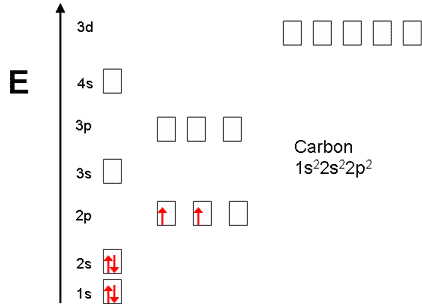
Orbital filling diagrams - The Cavalcade o' Chemistry 23.02.2016 · The orbital filling diagram for carbon. Again, we start with the electron configuration, which is 1s²2s²2p². As we’ve seen, this means that there are 2 electrons in the 1s orbital, two electrons in the 2s orbital, and two electrons in the 2p orbitals. This is shown like this:
Oxygen(O) electron configuration and orbital diagram Oxygen(O) is the 8th element in the periodic table and its symbol is ‘O’. This article gives an idea about the electron configuration of oxygen and orbital diagram, period and groups, valency and valence electrons of oxygen, bond formation, compound formation, application of different principles.Hopefully, after reading this article you will know in detail about this.
Qualitative molecular orbital diagram for MoC. The 10 orbital is... Download scientific diagram | Qualitative molecular orbital diagram for MoC. 8 There are several possibilities for the ground state. If the bonding interaction between the metal and carbon atoms becomes great enough at Zr, ZrC may be forced into the 10 2 11 2 5 4 , 1 ⌺ ϩ ground term.
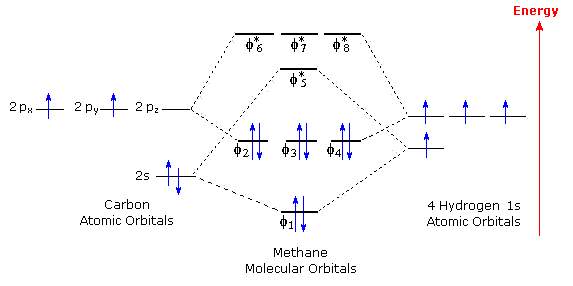
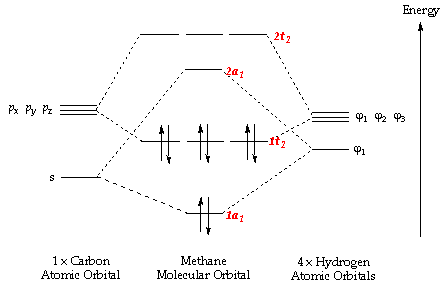
Global Carbon Cycle - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The global carbon cycle model describes the evolution of the mass of carbon in the mantle, Cm, in the combined reservoir consisting of ocean and atmosphere Figure 6.6 . The molecular orbital diagram for methane CH 4 illustrates how valence hydrogen and carbon atomic orbitals combine to form an...
Orbital Diagram For Carbon (C) | Carbon Electron Configuration... Carbon Electron Configuration. Chemistry is that subpart of science which is completely different from the other subjects and the students' needs to be very attentive and smart in order to clear their It becomes easier to solve questions that are related to the finding of Carbon Electron Configuration.
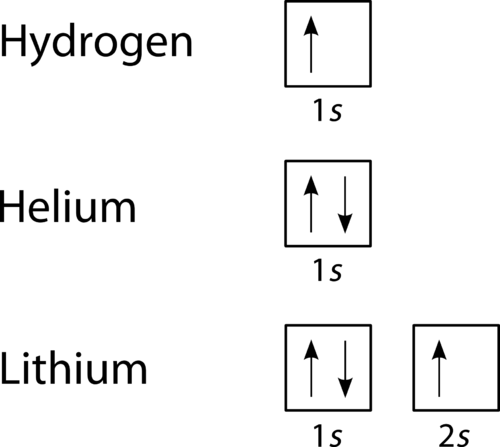
Orbital Diagrams Chemistry Tutorial Orbital Diagrams Chemistry Tutorial. Key Concepts. An orbital diagram, or orbital box diagram, is a way of representing the electron configuration of an atom. A box, line, or circle, is drawn to represent each orbital in the electron configuration (using the Aufau Principle to order the orbitals and hence...
PDF Microsoft Word - Chapter 1_6_SY.doc Carbon-carbon sigma bond rotation in butane occurs easily because a sigma bond has bonding electron density directly between two bonded atoms. The molecular orbital diagram for the second row homonuclear. Chapter 9. Theories of Chemical Bonding.
CN- lewis structure, molecular orbital diagram, and, bond ... Also, using the Molecular orbital diagram of CN-we can also find its bond order which helps us to predict its bond length and stability as well. Procedure to draw the molecular orbital diagram of CN. 1. Find the valence electron of each atom in the CN molecule. Clearly, carbon has 4 valence electrons and nitrogen has 5. 2.
electronic structure and atomic orbitals Orbits and orbitals sound similar, but they have quite different meanings. The diagram (not to scale) summarises the energies of the various orbitals in the first and second levels. The electronic structure of carbon. Carbon has six electrons. Two of them will be found in the 1s orbital close to the nucleus.
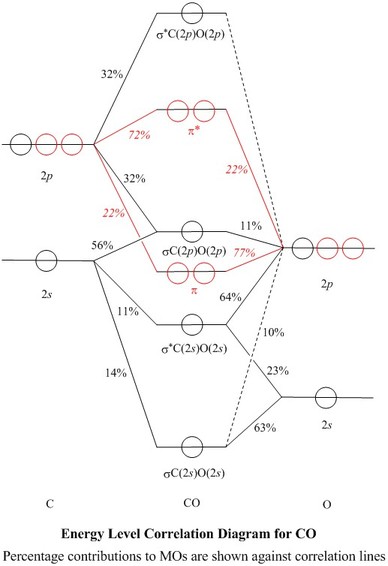
Molecular orbital diagrams for heteronuclear diatomic molecules The orbital diagrams may also look similar. A major difference is that the more electronegative atom will have orbitals at a lower energy level. Carbon monoxide is an example of a heteronuclear diatomic molecule where both atoms are second-row elements.
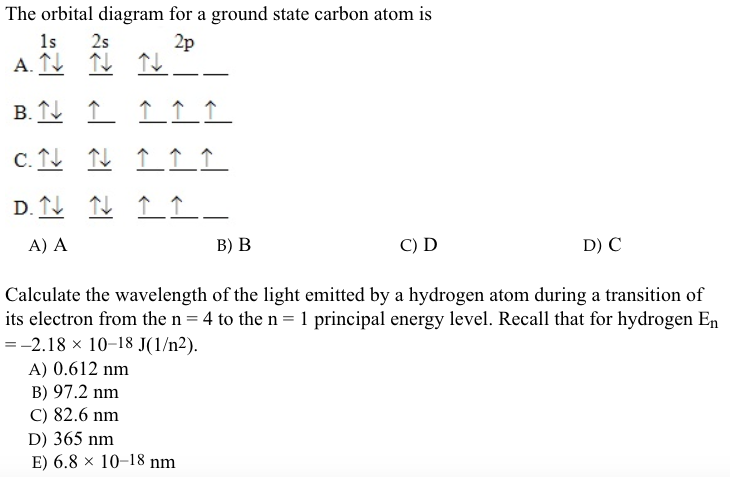
PDF Chapter 2 Atoms and Elements 5.4 Drawing Orbital Diagrams and Writing Electron Configurations. In the orbital diagram of carbon, two electrons occupy the 1s orbital, two electrons occupy the 2s orbital, and two electrons each occupy a 2p orbital in the 2p sublevel. 15 Basic Chemistry. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
Carbon Bohr Model - How to draw Bohr diagram for Carbon(C ... S orbital can hold maximum of 2 electrons and P orbital can hold maximum of 6 electrons. FAQ. How many electron shells a Carbon Bohr model contains? Electron shell also called energy level, you can find the number of electron shells for an element by knowing its period number in the periodic table. The elements or atoms in the first period of the periodic table have one energy …
Hybridization of Carbon - ppt video online download 4 Excited state orbital fill diagram of Carbon Carbon still has 6 electrons, but one of the s electrons "jumps" to a higher energy level. 1s 2s 2p 6 In 1931 Linus Pauling proposed HYBRIDIZATION, which explains HOW carbon forms 4 equivalent bonds; it does not explain WHY. The s and p orbitals...
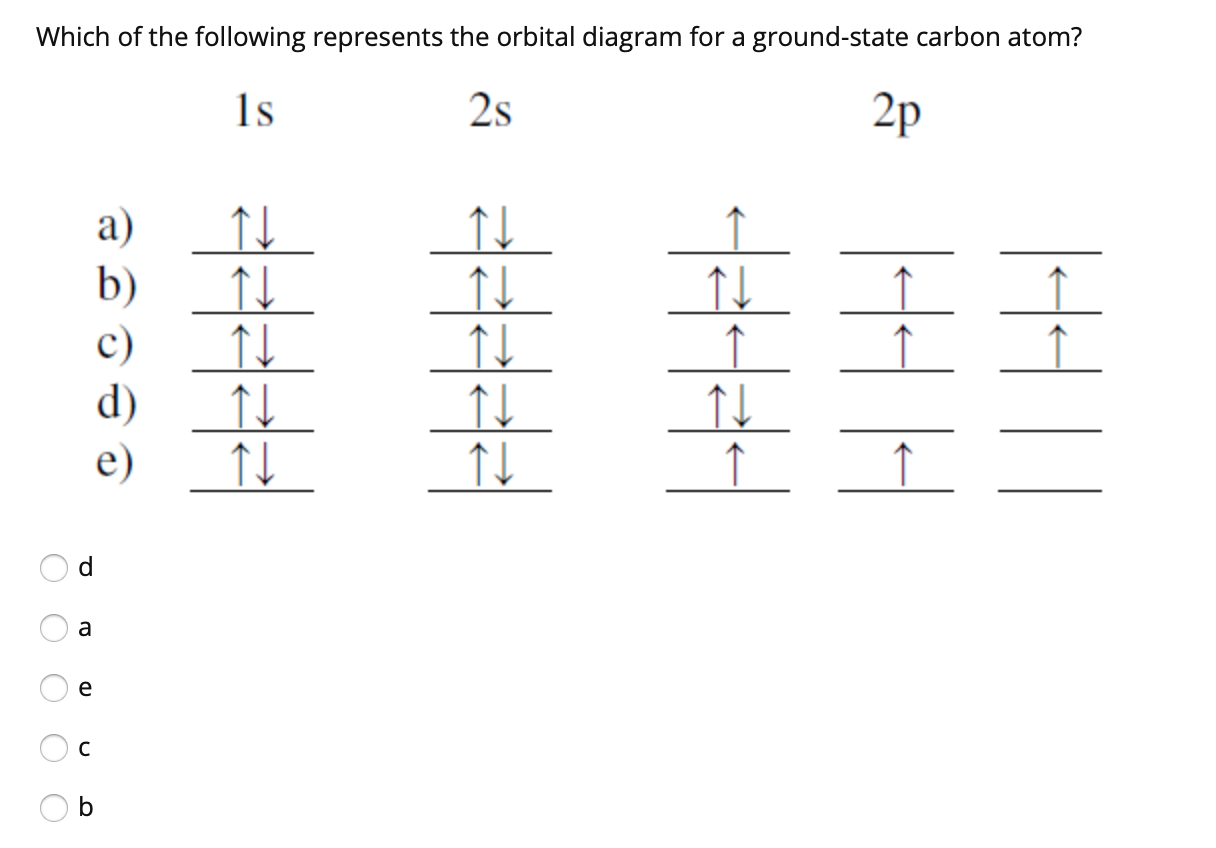
Which is the correct orbital diagram for carbon? - Brainly.com Carbon is a p-block element. The s-sublevel can only accommodate two maximum electrons because it has one orbital. This is why both 1s and 2s contains just two electrons each.
Introduction to Molecular Orbital Theory For the ethene orbital energy diagram these are shown as pCC for the HOMO, and p*CC for the LUMO. In all cyclic polyenes (CnHn), the p-molecular orbitals occur in degenerate pairs, except for the lowest p-orbital, and for the cyclic polyenes with even numbers of carbon atoms, the highest...
Orbital Diagram of All Elements (Diagrams given Inside) 10.04.2021 · Orbital diagram of Carbon (C) 7: Orbital diagram of Nitrogen (N) 8: Orbital diagram of Oxygen (O) 9: Orbital diagram of Fluorine (F) 10: Orbital diagram of Neon (Ne) 11: Orbital diagram of Sodium (Na) 12: Orbital diagram of Magnesium (Mg) 13: Orbital diagram of Aluminum (Al) 14: Orbital diagram of Silicon (Si) 15: Orbital diagram of Phosphorus (P) 16: …
Molecular Orbital Diagrams: Nitrogen, Carbon, and Boron - YouTube In this video we will draw the molecular orbital diagrams for diatomic nitrogen, carbon and boron. We will also calculate their bond order and determine if...
Molecular Orbital Theory | Boundless Chemistry Molecular orbital diagram for hydrogen: For a diatomic molecule, an MO diagram effectively shows the energetics of the bond between the two atoms, whose AO unbonded energies are shown on the sides. The unbonded energy levels are higher than those of the bound molecule, which is the energetically-favored configuration. Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals. A …
Give orbital diagram of carbon . FOR ONE MARKS - Brainly.in The orbital diagram shows how the electrons are arranged within each sublevel. ... In a neutral carbon atom, the 1s sublevel has one orbital with two electrons with opposite spins, represented by the arrows pointing in opposite directions.
PDF Organometallic Chemistry Prepare a molecular orbital energy level diagram of the peroxide ion, O22−, and predict the bond order of this ion. Group orbital 1 can interact with the 2pz orbital of carbon. (This interaction is likely to be weak, because the 2s orbitals of oxygen are much lower in energy than the 2p orbitals of carbon.)


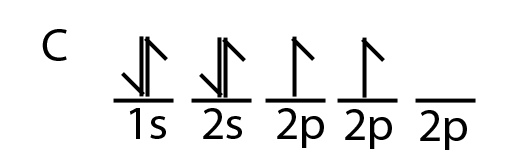








Comments
Post a Comment